R语言 朴素贝叶斯分类器①
本文共 2086 字,大约阅读时间需要 6 分钟。
-
朴素贝叶斯分类器原理:
这种学习方法基于条件概率,也就是通过已经给定的东西来推断一件事情的发生可能性。朴素贝叶斯应用了贝叶斯定理和朴素独立性假设。
- 优势
- 不相关特征不敏感
- 一次扫描就能快速训练
- 快速分类
- 能够处理任意数量的预测因子,不论他们是连续的还是分类的
- 尤其适合高维数据
- 劣势
- 假定了特征之间相互独立
-
朴素贝叶斯分类算法的实现函数
R中的e1071包中的naiveBayes函数可以实现朴素贝叶斯算法,具体的函数格式如下:naiveBayes(formula,data,laplace=0,subset)
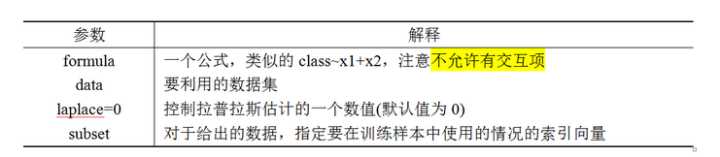
image
- 通过e1071包中的naiveBayes()函数,使用独立的预测变量,计算一个分类变量的条件后验概率。
setwd("E:\\Rwork")install.packages("e1071")library(e1071)index <- sample(nrow(iris),0.75*nrow(iris))train <- iris[index,]test <- iris[index,]nb1 <- naiveBayes(Species ~., data =train )prediction <- predict(nb1, test[,-5])xlab <- table(prediction , test$Species)xlabprediction setosa versicolor virginica setosa 40 0 0 versicolor 0 38 2 virginica 0 2 30 - gmodels包中的CrossTable函数可以来进行模型评估,得到的结果如下:
pre1 <- predict(nb1,test)a <- table(test$Species,pre1)(sum(a)-sum(diag(a)))/sum(a)b <- paste0(round((sum(a)-sum(diag(a)))*100/sum(a),2),"%")library(gmodels)CrossTable(test$Species,pre1,prop.r = FALSE, prop.c = FALSE,prop.t = TRUE,prop.chisq = FALSE) Cell Contents|-------------------------|| N || N / Table Total ||-------------------------| Total Observations in Table: 112 | pre1 test$Species | setosa | versicolor | virginica | Row Total | -------------|------------|------------|------------|------------| setosa | 40 | 0 | 0 | 40 | | 0.357 | 0.000 | 0.000 | | -------------|------------|------------|------------|------------| versicolor | 0 | 38 | 2 | 40 | | 0.000 | 0.339 | 0.018 | | -------------|------------|------------|------------|------------| virginica | 0 | 2 | 30 | 32 | | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.268 | | -------------|------------|------------|------------|------------|Column Total | 40 | 40 | 32 | 112 | -------------|------------|------------|------------|------------|
转载地址:http://jyncx.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
android大概是通过logcat拦截Log
查看>>
关于codeMirror插件使用的一个坑
查看>>
评论:人才流失强力折射出现实畸形人才观
查看>>
git服务器gitlab之搭建和使用--灰常好的git服务器【转】
查看>>
基于机器学习的web异常检测——基于HMM的状态序列建模,将原始数据转化为状态机表示,然后求解概率判断异常与否...
查看>>
分享一种需求评审的方案
查看>>
虚拟运营商10月或大面积放号 哭穷背后仍有赢家
查看>>
Server2016开发环境配置
查看>>
分布式光伏发电建设中的逆变器及其选型
查看>>
增强网络安全防御 推动物联网走向应用
查看>>
UML中关联,组合与聚合等关系的辨析
查看>>
《大数据管理概论》一3.2 大数据存储与管理方法
查看>>
PowerBuilder开发简单计算器
查看>>
怎样使用linux的iptables工具进行网络共享
查看>>
《HTML5与CSS3实战指南》——导读
查看>>
RHEL6下安装oracle 10g(一)
查看>>
Kconfig的格式
查看>>
关于Cursor的moveToFirst和moveToNext的意义
查看>>
个人--工资划分5份
查看>>
有关文件下载的文件名
查看>>